La gestión de Segregación de Funciones (SoD, Segregation of Duties) es uno de los pilares de control interno dentro de cualquier empresa que utilice SAP S/4HANA. Una mala definición de roles y autorizaciones puede exponer a la organización a fraudes, manipulación de datos, errores financieros y fallos en auditoría.
En S/4HANA, donde los procesos están más integrados que nunca (Order-to-Cash, Procure-to-Pay, Record-to-Report), la correcta segregación de funciones no solo es un requisito de compliance, sino una práctica esencial para proteger la integridad del sistema y mantener controles internos sólidos.
Este artículo te enseñará:
- Qué es una función SOD y por qué es tan importante.
- Cómo se generan conflictos SOD dentro de S/4HANA.
- Ejemplos reales de conflictos SOD en procesos integrados de negocio.
- Cómo implementar controles, mitigaciones y revisiones.
- Qué herramientas existen, como SAP GRC Access Control.
- Buenas prácticas para auditores, consultores y usuarios clave.
Todo con un enfoque práctico, claro y actualizado a la realidad 2025 de SAP S/4HANA.
Conceptos clave sobre SAP SOD
¿Qué es la Segregación de Funciones (SoD)?
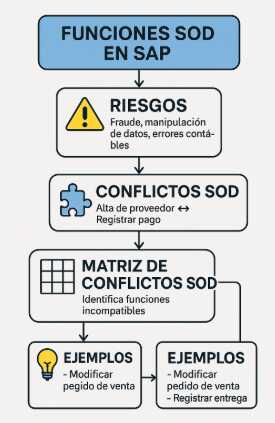
La Segregación de Funciones (SOD) es un principio de control interno que busca evitar que una misma persona pueda ejecutar todas las etapas críticas de un proceso de negocio.
Ejemplo simple:
Una persona no debe poder crear un proveedor y también aprobar el pago a ese proveedor.
Esto reduce los riesgos de:
- Fraude
- Pagos indebidos
- Manipulación de datos
- Errores contables
- Incumplimientos de auditoría interna y externa
¿Qué es un conflicto SOD?
Un conflicto SOD ocurre cuando un usuario tiene permisos que combinados pueden resultar peligrosos o permitir acciones indebidas.
Ejemplo típico en SAP:
| Riesgo | Función 1 | Función 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Pago fraudulento | Crear proveedor (P2P) | Registrar y liberar pago |
Si un usuario controla ambas actividades, el riesgo es evidente.
¿Qué es una matriz SOD?
Es un documento (generalmente una matriz tipo Excel o configurada en GRC) que define:
- Los procesos clave (O2C, P2P, R2R, fabricación).
- Las funciones críticas dentro de cada proceso.
- Los pares de funciones que, combinadas, representan un conflicto SOD.
Ejemplo reducido:
| Proceso | Función A | Función B | Riesgo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Procure-to-Pay | Alta de proveedor | Contabilizar pago | Pago indebido |
Importancia de SOD en SAP S/4HANA
En S/4HANA, los procesos están completamente integrados y el Universal Journal (ACDOCA) centraliza la contabilidad. Esto hace que:
- Una sola acción puede impactar múltiples áreas.
- Un conflicto SOD puede propagarse más rápido que en ECC.
- Los roles Fiori tienden a agrupar más funcionalidades, lo cual aumenta el riesgo si no se manejan correctamente.
Por esta razón, las empresas deben reforzar los controles preventivos, las revisiones periódicas y la limpieza constante de roles.
El rol de SOD dentro de los procesos de negocio integrados
En Procure-to-Pay (P2P)
El proceso de compras involucra múltiples etapas, desde la creación del proveedor hasta el pago final.
Ejemplos de conflictos SOD:
- Crear proveedor + modificar datos bancarios
- Crear pedido de compra + crear factura
- Registrar factura + liberar pago
Riesgo: desvío de fondos o pagos no autorizados.
En Order-to-Cash (O2C)
El ciclo de ventas requiere controles para evitar manipulación de precios o condiciones comerciales.
Ejemplos:
- Crear cliente + modificar condiciones de pago
- Crear pedido + registrar entrega + facturar
- Crear factura + registrar nota de crédito
Riesgo: manipulación de ingresos o descuentos indebidos.
En Record-to-Report (R2R)
Es el proceso contable donde se generan los estados financieros.
Ejemplos SOD:
- Contabilizar asientos + modificar cuentas contables
- Ejecutar cierre contable + modificar tipos de cambio
- Contabilizar ajustes + aprobar asientos manuales
Riesgo: distorsión de resultados financieros.
Gestión de funciones y roles en SAP S/4HANA
Roles Fiori vs Roles tradicionales (ECC)
En S/4HANA:
- Los accesos están orientados a catálogos y grupos Fiori.
- Las apps agrupan funciones más amplias que las viejas transacciones.
- Un rol Fiori mal diseñado puede incluir demasiadas capacidades críticas.
Por ello, la matriz SOD debe ser revisada y actualizada para S/4HANA, no simplemente “mostrada igual” que en ECC.
Autorizaciones basadas en objetos
SAP sigue utilizando objetos de autorización. Para reducir riesgos:
- No basta bloquear el menú o la app Fiori.
- Hay que controlar los objetos de autorización asignados a cada usuario.
- Es clave revisar valores como sociedad, clase de documento, tipo de transacción, etc.
¿Cómo se detecta un conflicto SOD?
1. Análisis manual
Revisando la matriz SOD y comparando roles asignados al usuario.
2. Análisis automatizado en SAP GRC Access Control
La forma más avanzada y recomendada.
GRC permite:
- Escanear roles y usuarios.
- Identificar conflictos SOD automáticamente.
- Proponer controles compensatorios.
- Gestionar aprobaciones y auditoría.
3. Auditoría externa / interna
Los auditores revisan:
- Accesos críticos
- Historial de aprobaciones
- Cambios en roles
- Evidencia de controles compensatorios
Ciclo de vida de un conflicto SOD
-
Identificación
Detectar que un usuario posee dos funciones incompatibles. -
Evaluación del riesgo
Determinar el nivel de criticidad. -
Decisión
- Mitigar
- Remediar
- Aceptar riesgo (excepción documentada)
-
Implementación de la medida
- Ajustar roles
- Asignar control compensatorio
- Revisar periodicidad
-
Monitoreo continuo
- Revisiones trimestrales
- Auditorías automáticas GRC
- Reportes segmentados por proceso
Ejemplos reales de conflictos SOD por proceso
Procure-to-Pay (P2P)
| Función | Función conflictiva | Riesgo |
|---|---|---|
| Crear proveedor | Modificar datos bancarios | Pago fraudulento |
| Crear pedido | Registrar factura | Aprobación indebida |
| Registrar factura | Liberar pago | Pagos no autorizados |
Order-to-Cash (O2C)
| Función | Función conflictiva | Riesgo |
|---|---|---|
| Crear cliente | Modificar forma de pago | Créditos indebidos |
| Cambiar precio | Crear pedido | Manipulación comercial |
| Registrar factura | Registrar nota de crédito | Descuentos indebidos |
Record-to-Report (R2R)
| Función | Función conflictiva | Riesgo |
|---|---|---|
| Contabilizar asientos | Modificar cuentas contables | Fraude contable |
| Modificar tipo de cambio | Registrar transacciones en divisas | Manipulación de cierre |
| Crear activo fijo | Dar de baja activo | Pérdida o robo de activos |
Errores frecuentes y buenas prácticas
Errores frecuentes
-
Copiar roles ECC a S/4HANA sin revisar apps Fiori
Resultado: roles sobrecargados. -
No utilizar matriz SOD específica por industria
Riesgo: controles incompletos. -
Asignar roles de emergencia sin expiración automática
Problema: accesos críticos permanentes. -
No documentar excepciones ni controles compensatorios
Auditorías fallidas.
Buenas prácticas
-
Diseñar roles por tarea, no por usuario
Evita roles duplicados y permisos innecesarios. -
Actualizar matriz SOD cada año o con cada release SAP
Por nuevas apps y procesos. -
Usar SAP GRC Access Control como herramienta principal
- Análisis de riesgo
- Workflow de aprobaciones
- Registro histórico
- Remediación automática
-
Aplicar controles compensatorios cuando no se pueda remover un conflicto
Ejemplos:- Revisión diaria de reportes
- Doble firma
- Auditoría digital
-
Implementar un proceso formal de “Emergency Access Management”
Controlado, auditado y con expiración automática.
Preguntas frecuentes (FAQ)
1. ¿Qué es un conflicto SOD en SAP?
Es cuando un usuario tiene dos permisos que, combinados, pueden generar un riesgo operativo o de fraude.
2. ¿SOD solo aplica a SAP FI?
No. Afecta todos los procesos: compras, ventas, logística, finanzas, activos fijos, tesorería y más.
3. ¿Se puede trabajar sin SAP GRC?
Sí, pero no es recomendable. Sin GRC, la gestión SOD es manual y muy difícil de auditar.
4. ¿Los roles Fiori reducen el riesgo SOD?
No necesariamente. Algunos roles Fiori incluyen más funciones de las que parece. Hay que analizarlos cuidadosamente.
5. ¿Qué hacer si un conflicto no se puede resolver?
Implementar un control compensatorio, documentarlo y revisarlo periódicamente.
Conclusión
La gestión de Funciones SOD en SAP S/4HANA es fundamental para garantizar la seguridad, integridad y confiabilidad de los procesos de negocio. En un sistema tan integrado como S/4HANA, una mala asignación de roles puede generar riesgos severos que afecten la operación, la contabilidad y el cumplimiento normativo.
Dominar SOD implica:
- Entender los procesos de negocio (O2C, P2P, R2R).
- Conocer las funciones críticas de cada área.
- Diseñar roles limpios y bien estructurados.
- Utilizar herramientas como SAP GRC para análisis continuo.
- Mantener controles compensatorios donde sean necesarios.
Si trabajas como consultor, auditor, analista de seguridad o usuario clave, este conocimiento es indispensable para garantizar un sistema SAP robusto, auditado y seguro.
Consultoría-SAP
Consultoría SAP es un portal de información en español sobre todo lo relacionado al ERP SAP y ha creado este contenido tomando varias colaboraciones de sus miembros activos en la mayor comunidad de ayuda SAP del mundo.
![]() Novedad: hemos lanzado una nueva lista de correo para conversar de negocios, ERP, SAP y otros temas relacionados. Súmate ahora: https://masnegocios.substack.com
Novedad: hemos lanzado una nueva lista de correo para conversar de negocios, ERP, SAP y otros temas relacionados. Súmate ahora: https://masnegocios.substack.com

 A través de Segu.info me entero que Andreas Wiegenstein a través de
A través de Segu.info me entero que Andreas Wiegenstein a través de 







